
HMRC Late Payment Penalties: What UK Accountants Must Know in 2026
HMRC, a regulatory body in the UK, is authorised to impose penalties on establishments for late tax payments. HMRC imposes late penalties on UK businesses and individuals who fail to pay taxes such as VAT, corporation tax, PAYE, and self-assessment tax returns on time. These penalties include fixed charges, interest, and additional fines on the duration of the delay.
As an accounting practice, it will be your top priority to avoid these penalties, which can be detrimental both financially to your clients and reputationally to your practice. 2026 is the year when deadlines have become tighter, and compliance requirements while handling your client’s tax obligations have become stricter.
In this guide, we will cover the critical details accountants must stay updated on to navigate late payment penalties effectively this year.
- Understanding how HMRC enforces late payment penalties
- Latest Thresholds
- Mitigation strategies to protect clients from avoidable fines and interest charges
Let’s understand and learn how to avoid this costly mistake.
What Are HMRC Late Payment Penalties in 2026?
In 2026, HMRC late payment penalties refer to fines imposed on businesses and individuals in the UK who fail to pay their tax liabilities on time. These additional penalties apply to various taxes, including VAT, corporation tax, self-assessment tax returns, and PAYE.
Since 28th May 2025, HMRC charges interest at 8.25% on late payments, linked to the Bank of England base rate plus 4%. This late payment interest rate applies across various tax obligations, including VAT late payment interest.
Currently, HMRC is implementing a new penalty point system that will significantly change the UK tax compliance. Here’s what’s changing in HMRC’s penalty points system:
| Time Period | Penalty Rate | Additional Charges |
| 30 days late | 5% of unpaid tax | Interest charges apply |
| 6 months late | Additional 5% | Ongoing interest |
| 12 months late | Further 5% | Compound interest |
How Late Payment Interest Works for UK Businesses
UK businesses are charged interest on late payment of their tax liabilities by HMRC. The reason behind this is to encourage timely payments.
Here is how it works:
- Late payment interest applies to various taxes, including VAT, corporation tax, PAYE, and self-assessment tax returns.
- Interest is charged from the day after the payment due date until the full payment is made. For example, if VAT is due on the 7th of the month, interest starts from the 8th if it is unpaid.
- The interest is calculated on a daily basis, so the longer the delay, the more interest accrues.
- HMRC’s late payment interest rate is linked to the Bank of England base rate, typically set at the base rate plus 2.5%. This rate can change in line with adjustments to the base rate.
Understanding these points can help you in making your clients stay compliant and manage their cash flow effectively.
HMRC Fines for Late Payment Across VAT, Corporation Tax & PAYE
In 2025, HMRC will enforce strict penalties for late tax payments, affecting UK businesses across VAT, Corporation Tax, and PAYE obligations. These fines are designed to encourage prompt compliance and can have a significant impact on a business’s financial health if overlooked. Let’s take a close look at it.
1. VAT Late Payment Penalties
Late payment of VAT before the due date will lead to penalties, except:
- VAT payment on account
- Instalments for the VAT Annual Accounting Scheme
For late payment penalties, the sooner you pay, the lower the penalty amount will be.
For payment up to 15 days overdue
There is no penalty for the first late payment, and a penalty is charged for the second late payment.
Payment between 16 and 30 days overdue
The first late payment penalty is calculated at 3% of the VAT you owe as of day 15.
Payment 31 days or more overdue
The first late payment penalty is calculated as 3% of the outstanding amount at day 15, plus 3% of the outstanding amount at day 30.
The second late payment penalty is calculated at a daily rate of 10% per year on the outstanding balance. This charge is applied daily, from day 31, until the outstanding balance is paid in full.
2. Corporation Tax Late Payment Penalties
The HMRC fines for late payment on corporation tax are as follows:
| Time after your deadline | Penalty |
| 1 day | £100 |
| 3 months | Another £100 |
| 6 months | HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) will estimate your Corporation Tax bill and add a penalty of 10% the unpaid tax |
| 12 months | Another 10% of any unpaid tax |
3.PAYE Late Payment Penalties
HMRC applies late payment penalties on PAYE amounts that are not paid in full and on time. These include monthly, quarterly, or annual PAYE, student loan deductions, Construction Industry Scheme (CIS) deductions, and Class 1 National Insurance contributions (NICs), among others.
The penalty structure on late PAYE payments is as follows:
| Number of defaults in a tax year | Penalty percentage applied to the amount that is late in the relevant tax month |
| 1 to 3 | 1% |
| 4 to 6 | 2% |
| 7 to 9 | 3% |
| 10 or more | 4% |
HMRC will not count the first failure to make payments on time as a default.
If quarterly or monthly payments have not been made even after 6 months, then an additional penalty of 5% will be charged on the amount unpaid. A further penalty of 5% will be charged if payment is not made within 12 months.
Why Accountants Must Prioritise Late Payment Risk Management
There is a risk associated with late tax payments, which can lead to financial losses for your clients and reputational damage to your practice. Hence, a proper risk management plan must be in place to address delayed tax payments.
Here are some reasons why:
Financial Impact on Clients
Without proper risk management, late payment penalties and interest charge from HMRC have the potential to reduce your clients’ business profits and disrupt their cash flow, causing significant trouble.
Risk of Non-Compliance
Failing to meet due date payment deadlines will lead to compliance issues, which may bring unnecessary attention from HMRC to your clients and potentially trigger an audit.
Client Trust and Retention
Without proactively managing the risks involved in late tax payments, you will lose your client’s trust. By developing a mechanism that sends reminders for paying taxes well before the deadline, it will be widely appreciated by your clients. Such a measure will protect your clients from fines and maintain regulatory compliance.
Reputation Management
Frequent late payments for crossing the tax due date will not only tarnish the image of your clients but also that of your practice, making it harder for you to attract new business.
Operational Efficiency
By managing late payment risks, you can streamline workflows, reduce last-minute payment scrambles for your clients, and focus on advisory services, thereby enhancing client value.
5 Proactive Steps to Help Clients Avoid HMRC Late Payment Penalties
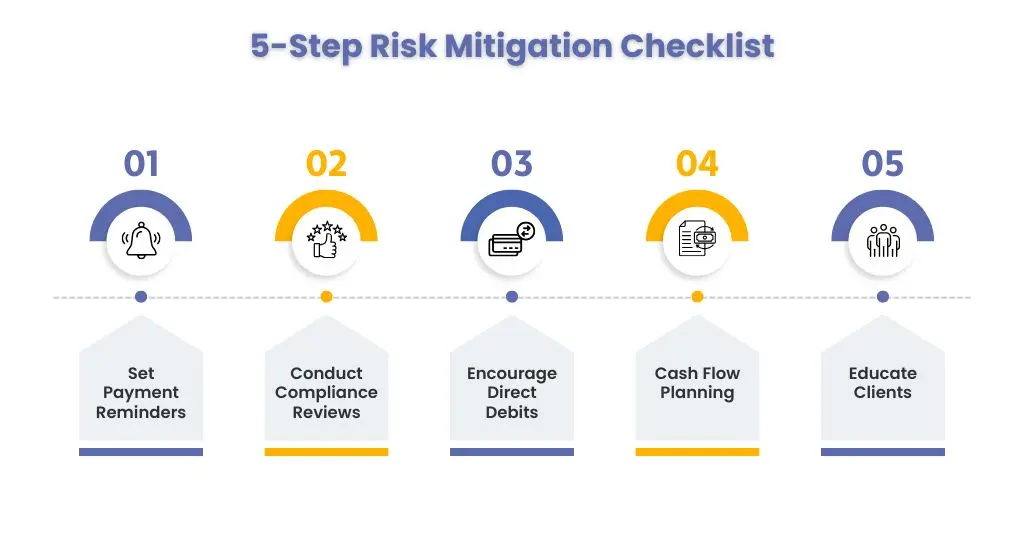
HMRC will not take late payment of taxes lightly, so it is up to you to devise ways that will safeguard your clients from these penalties and ensure full compliance with deadlines and regulations. We have listed five steps which will get the job done.
Set Up Payment Reminders
Utilize the best accounting software to implement automated reminders that notify your clients, ensuring they make VAT, corporation tax, and PAYE payments before the deadlines. These reminders will ensure that your clients avoid additional penalties for missing deadlines.
Regular Compliance Reviews
Always perform a thorough review of your client’s financial records, as this will help identify and rectify discrepancies or overdue payments, thereby saving your clients from filing penalties.
Encourage Direct Debits
Setting up a direct debit arrangement with HMRC is necessary, which will reduce manual errors and ensure timely and consistent payments.
Provide Cash Flow Planning Support
You must take steps to manage your cash flow so that enough funds are available to fulfil tax obligations, thereby minimising the risk of missing payments.
Educate Clients on Penalty Structures
Work on organising workshops with your clients to enhance their understanding of how HMRC calculates late payment interest and fines. Such an awareness campaign will encourage your clients to give compliance importance and avoid additional penalties.
Case Study: How We’ve Helped UK Accountants
We understand that HMRC regulations are becoming increasingly complex, making it difficult for practices to handle them alone. In such a case, you must, without any delay, choose a professional accounting outsourcing services of a provider for support, like Corient.
Here are some case studies where corient has helped its clients:
How Corient Solved a VAT Processing Crisis for a Financial Company
Challenges Faced:
- Struggled with a high volume of VAT-related queries
- Clients were either unresponsive or delayed in providing necessary documentation
- Bottlenecks in the VAT input claim process risk late VAT filings
What They Did:
- Minimised client queries by extracting data directly from Amazon and online sales channels.
- Verified clients’ VAT statuses to ensure accurate processing tailored to business types.
- Streamlined invoice management, especially for clients without VAT obligations.
Surprise Hurdle
- Clients still failed to provide complete or consistent documents
How was it fixed
- Checklist to gather all essential client credentials at the start
- Email templates and follow-ups for documentation
- Direct access to client sales platforms and invoice portals for more efficiency and accuracy
- Conduct scheduled reviews incorporating new business scenarios or client requirements.
Results
- Query volumes decreased by over 60%
- Turnaround time for VAT filings improved by 40%
- Improvement in cash flow predictability and regulatory confidence among clients.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The current late payment and repayment interest rates applied to the main taxes and duties that HMRC currently charges and pays interest on are 8.25% from 28 May 2025.
HMRC begins applying late payment penalties as soon as specific time thresholds are crossed:
For VAT, the first late payment penalty is calculated at 3% of the VAT you owe as of day 15.
For corporation tax it is:
1 Day Late: An initial fixed penalty of £100.
3 Months Late: An additional fixed penalty of £100.
6 Months Late: HMRC estimates the corporation tax bill and adds a penalty of 10% of the unpaid tax.
12 Months Late: A further 10% penalty on any remaining unpaid tax.
No, HMRC does not count the first failure to make payments on time as a default.
Late payment interest = (Unpaid Amount) × (Interest Rate) × (Number of Days Late) ÷ 365. The rate for 2025 is 8.25% per annum.
Here is a clear requirements of what self-employed directors of UK limited companies must follow:
a. Register for Self-Assessment (SA1)
b. Take a Salary Under PAYE
c. Maintain Proper Company Records
d. Prepare & File Annual Accounts
e. Pay Corporation Tax
f. Declare Dividends Properly
g. Register for VAT (if applicable)
h. Comply with Employment Law Requirements
i. Follow Companies Act 2006 Director Duties
Conclusion
Accounting practices have increasingly faced frequent headaches due to HMRC’s late tax payment penalties in recent years, but they can convert this challenge into an opportunity. The purpose of this guide is to inform you about how late payment interest works, HMRC Fines for Late Payment across taxes, how to mitigate the risk, and how to proactively avoid late tax due payments.
Prioritising these measures not only protects clients from unnecessary expenses like penalty for late payments but also enhances the reputation and reliability of accounting practices in an increasingly compliance-driven environment.
There is also another way to avoid late payment of taxes and their filing penalties: opting for outsourcing. Under outsourcing, you will be choosing a capable outsourcing accounting service provider who will handle your clients’ VAT, Corporation Tax, and PAYE filing and payments, thus ensuring accuracy and timely payments. Now, multiple service providers are offering their outsourcing services, but Corient is one you should look out for.
Established in 2011, Corient has gained considerable trust in accounting practices in the UK for offering up-to-date accounting services, including VAT, payroll, corporation tax, and bookkeeping outsourcing services. Our accounting outsourcing services have helped practices in saving their clients from costly penalties and streamlined their tax payments. Contact us to schedule your free consultation.


